14 AI projects to watch: Mozilla’s first Builders Accelerator cohort kicks off
We launched the Mozilla Builders Accelerator with the theme of local AI back in June. Our goal was to spark innovation in the AI ecosystem. Now, 14 exciting projects are leading the charge.
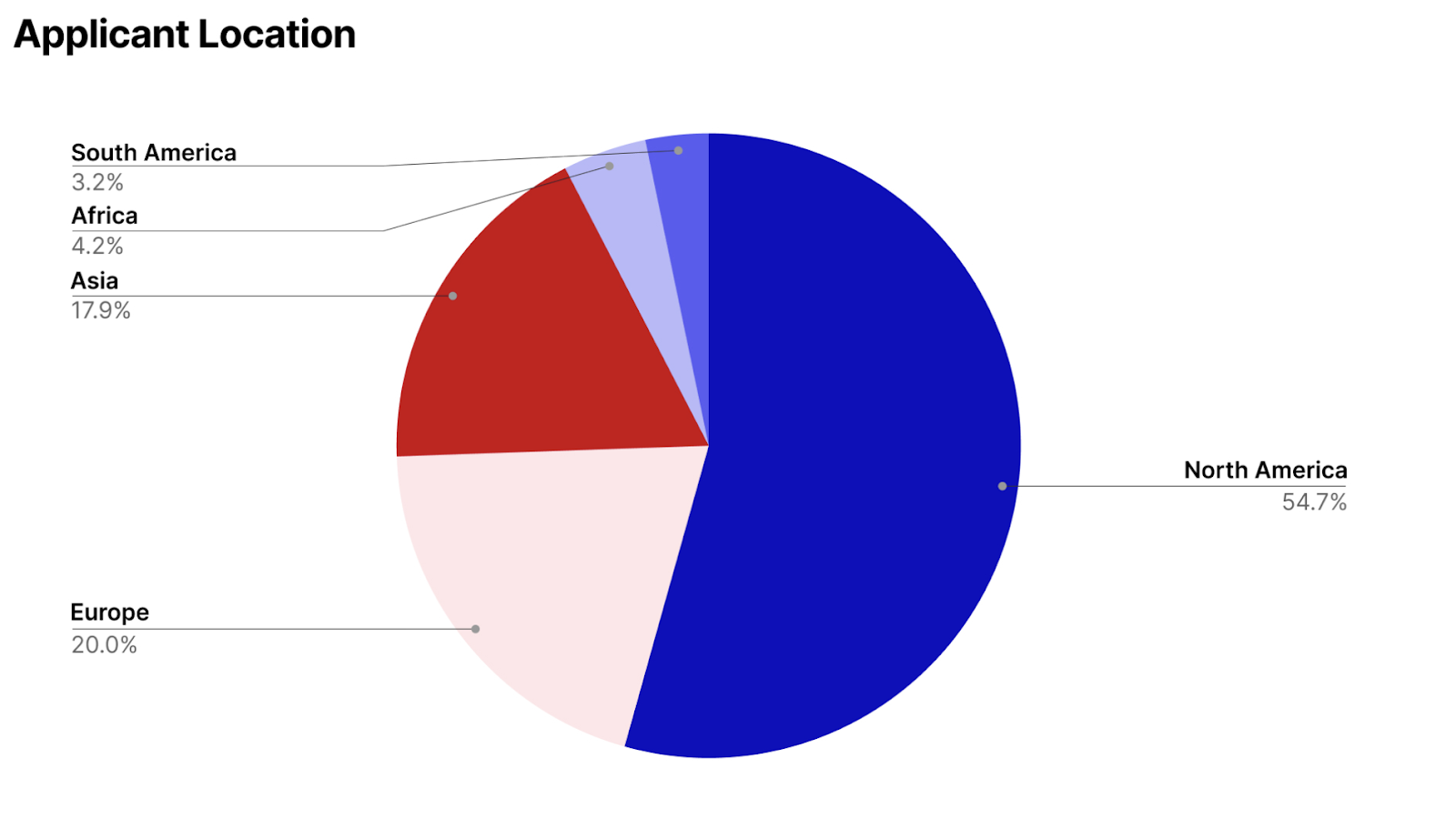
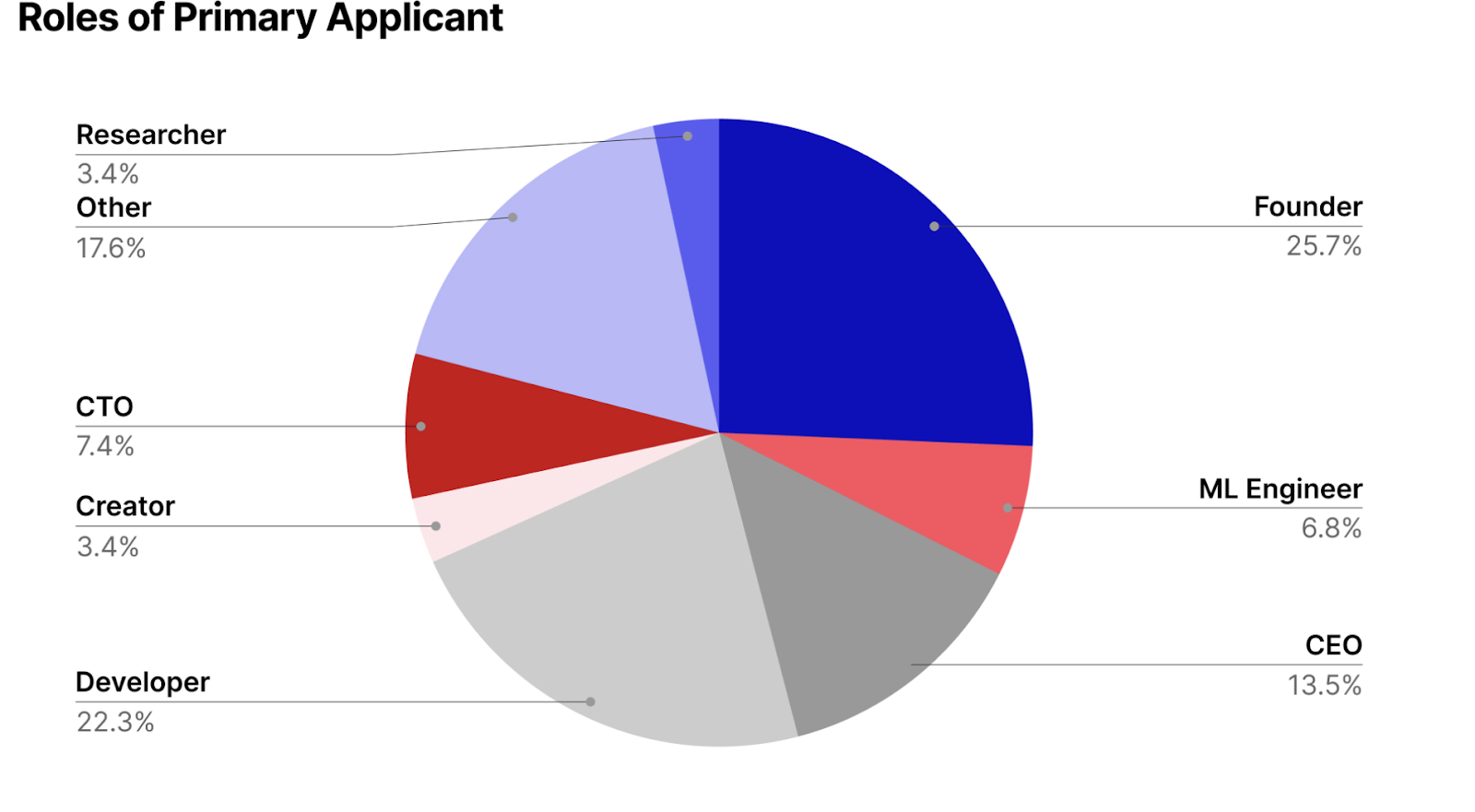
Calling on AI and machine learning engineers passionate about open source and local AI, nearly 200 applicants from 44 countries stepped up to push the boundaries of what’s possible with running models directly on personal devices instead of relying on the cloud. After a rigorous review process, we’re thrilled to announce the 14 groundbreaking projects that made the cut, each earning up to $100,000 in funding and mentorship from Mozilla.
“When we first opened applications, we weren’t sure how many would dive in, given that local AI is still a relatively new concept. But the open-source community proved its strength and potential beyond our expectations,” said Liv Erickson, who leads ecosystem development at Mozilla. “These 14 projects stood out with their creativity, potential impact on the local AI tech stack, and alignment with Mozilla’s values.”
Accelerating AI with purpose
When you think “accelerator,” you might picture a fast-paced, high-stakes startup scene. That works for some, but we’re doing it the Mozilla way – focusing on what really matters: keeping the internet open and accessible to all.
We’ve tailored the Mozilla Builders Accelerator to support a diverse group of innovators – from students with groundbreaking ideas to seasoned CTOs with high-potential side projects. This approach lets us zero in on the best ideas, while still offering the structure, funding, mentorship and demo day you’d expect from an accelerator.
Meet Mozilla Builders Accelerator’s first cohort
During the review process, three key categories stood out: application and training/fine-tuning, developer tools and infrastructure enhancement, and expressive media and data visualization projects. Here’s a breakdown of categories and projects.
Application and training/fine-tuning
Projects that focus on improving and customizing AI models for better performance and real-world use.
- Instant pronunciation feedback with a language coach from Koel Labs – Using movie scenes to improve pronunciation in real-time, Koel Labs offers grammar feedback through an AI-powered language coach. The app ensures privacy and accessibility all while running locally.
- A Large Language Model (LLM) for Swahili by Sartify – Designed to provide general and domain-specific AI capabilities for Swahili-speaking regions, Sartify’s Swahili-LLM supports multilingual interactions in East Africa. The goal is to make AI more accessible and drive inspiration within these communities to engage in AI research and development.
- Making scientific data accessible to all with ScholasticAI from Pleias – Helping users access high-quality scientific data in multiple languages, ScholasticAI uses open-source AI models to process open licensed scientific documents. Top-tier research is more accessible all while ensuring privacy and reducing the need for remote servers.
- Simplifying large language model tools from Transformer Lab – Making tasks like training, fine-tuning, and evaluating LLMs simple and accessible, Transformer Lab helps developers and researchers get started quickly. It builds and manages large language models (LLMs) on Windows, MacOS, and Linux, thus lowering the barrier to entry for working with LLMs. It supports various frameworks and offers powerful features within a single application.
Developer tools and infrastructure enhancement
Tools and systems that make software development easier and more powerful, helping developers build and manage their projects more effectively.
- Curating AI/ML models for drug discovery research in low- and middle-income countries from Ersilia Model Hub – Focusing on critical diseases, Ersilia Model Hub provides AI/ML tools that operate locally, ensuring access even in areas with poor internet connectivity. Their goal is to improve researcher access for drug discovery in the Global South.
- Building agents to make software deployment easier from Foyle – Using a notebook format to simplify automation and operations tasks across workflows, Foyle is an AI copilot that learns from continuous feedback.
- Enhancing control and understanding of AI models from K Sadov – Feature Retrieval, Editing, and Understanding for Developers (FREUD) helps developers better control and understand AI model outputs by focusing on the interpretability of speech-to-text models like Whisper. Using sparse autoencoders (SAE) to decompose model features, the project will explore latent capabilities in Whisper models, such as speaker emotion detection and diarization. FREUD will also provide user-friendly tools and an interface to navigate and analyze these features.
- PDF data extraction from Marker – Using advanced OCR for layout, text, and math detection, Marker converts PDFs to Markdown all running locally. This ensures high-quality data extraction without needing constant internet access. Paired with companion tools Surya and Texify, Marker helps create robust training datasets and improves data processing efficiency.
- Building a cutting-edge distributed ML framework with Elixir from Nx – Creating a scalable, distributed machine learning framework that outperforms current solutions, the Nx project leverages Elixir’s unique strengths in multitasking and fault-tolerance. By automatically spreading tasks across multiple devices, Nx aims to deliver a more scalable and efficient solution.
- Community collaboration tools from Open WebUI – Open WebUI is an easy-to-use interface that lets you run powerful GPT-like AI models without an internet connection. Originally designed to enhance AI tools, it has become a popular platform with over 3 million downloads. Now, the focus is on building a community where users can share data and insights to improve AI models together.
- Editable copilot capabilities from Theia AI IDE – Offering full transparency, customizable prompts, and the freedom to choose and host their own language models, Theia AI IDE extends the existing Theia editor to provide a suite of copilot options and agents for developers to customize their tools and workflows with on-device or cloud AI solutions.
Expressive media and data visualization
Creative projects that find new ways to display data and media, making information easier to understand and more engaging.
- Data clustering and visualization from Latent Scope – Using advanced AI to categorize, cluster, and explore large, unstructured datasets through an intuitive interface, Latent Scope runs locally or integrates with popular AI models, offering flexibility and accessibility that unlocks new insights into your datasets.
- A creative tool for interactive art from Tölvera – Artists can create and interact with dynamic, self-organizing systems with Tölvera. Inspired by artificial life, it’s a Python library that allows users to combine built-in behaviors like flocking and swarming or create their own, making it a powerful tool for creative expression.
- On-device semantic search and image recognition from Ente – Providing users with private, durable, and reliable photo storage, Ente Photos is a fully open source platform for storing family photos securely.
Mozilla’s efforts to build and deploy AI adhere to our mission of 25 years – putting people first, while being truly trustworthy and open. Our role is to advocate for better AI by unlocking resources for smaller, mission-minded builders and offering products incorporating AI solutions for safer digital experiences. The Mozilla Builders Accelerator is a key step forward, and we’re excited to see where these projects go.
Sign up for our newsletter for updates as we follow our participants’ journeys, and if you’re as passionate as we are about the future of open-source AI, there are plenty of ways to get involved – whether by supporting these projects or bringing your own ideas to the table in the next round of applications.
Let’s build the future of AI together, one open-source project at a time.